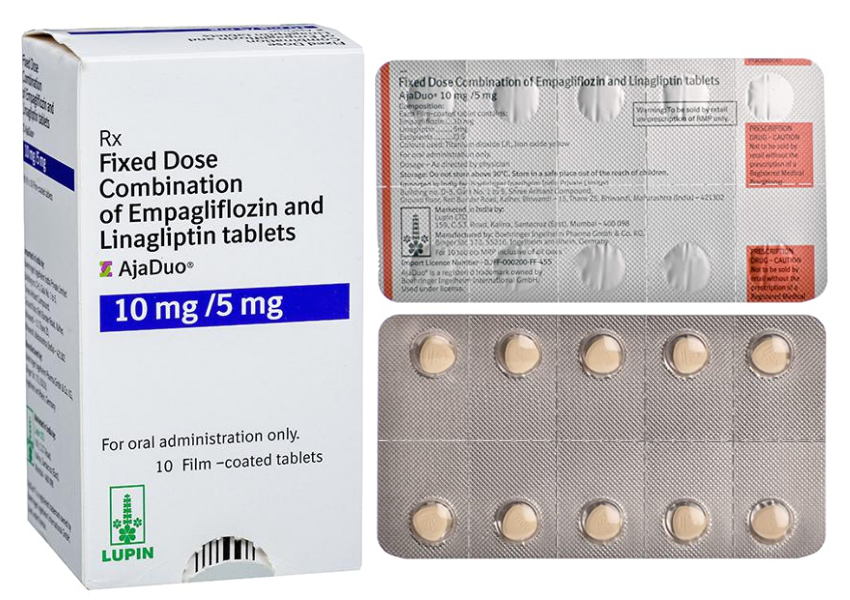
Buy AjaDuo®10mg/5mg Online
- Brand: Glyxambi
- Generic name: AjaDuo®
- Composition: Empagliflozin 10mg + Linagliprin 5mg
- Excipients: Q.S.
- Power: 15mg
- Disease/Treatment: Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Manufacturer: LUPIN LTD
- Country of Origin: India
Order AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg Tablet
AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg is indicated in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus as a supplement to diet and exercise in order to improve glycemic control.
Each film-coated tablet contains: Empagliflozin 10 mg, Linagliptin 5 mg, covered with a film shell of light pink color, triangular with rounded corners, flat with beveled edges.
The combination of Empagliflozin and Linagliptin is used to treat type 2 diabetes, which helps control glycemia. Empagliflozin is activated and helps eliminate glucose throughout the blood circulation. AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg is used in association with dietary regimen and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Packing: 10 tablets in 1 strip
- Minimum order quantity: 30 tablets
- Minimum price: $ 5.50 per tablet
- : 14-21 days
- Trackable service: 5-9 days
- Order from $150.00: Free AirMail shipping
AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg Dosage
AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg tablet is taken orally, regardless of food intake, at any time of the day.
The recommended initial dose is 5 mg of linagliptin + 10 mg of empagliflozin 1 time / day. If this dose is well tolerated, but does not provide adequate glycemic control, you can increase the dose to 5 mg of linagliptin + 25 mg of empagliflozin 1 time / day.
When using AjaDuo®10mg/5mg with insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of insulin / sulfonylurea derivatives in order to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Contraindications AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg:
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus;
- diabetic ketoacidosis;
- renal insufficiency with persistent GFR <45 ml/min / 1.73 m2;
- pregnancy, lactation (breastfeeding);
- age over 85 years;
- age under 18 years (due to insufficient data on efficacy and safety);
- hypersensitivity to the components of the combination.
With caution:
- Patients at risk of hypovolemia (use of antihypertensive drugs with a history of arterial hypotension);
- for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract leading to fluid loss;
- age over 75 years;
- use in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives or insulin;
- infections of the genitourinary system;
- a low-carb diet;
- diabetic ketoacidosis in the anamnesis;
- history of pancreatitis;
- low secretory activity of pancreatic beta cells.
How to take AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg tablets?
Recommended starting dose of AjaDuo® it is 5 mg of linagliptin + 10 mg of empagliflozin once a day, orally.
Patients who tolerate AjaDuo® well at a dose of 5 mg + 10 mg, if it is necessary to improve glycemic control, the dose can be increased to 5 mg of linagliptin + 25 mg of empagliflozin once a day.
When transferring a patient from therapy with empagliflozin and linagliptin monopreparations, AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg should be prescribed with the same daily doses of empagliflozin and linagliptin that the patient received in the form of monopreparations. Metformin should also be continued at the same dose.
AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg can be taken regardless of food intake, at any time of the day.
If you miss taking AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg
If you miss the next dose of the drug, if there are 12 hours or more left before the next dose, the patient should take AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg as soon as he remembers about it.
If there are less than 12 hours left before the next dose of the drug, the drug should be skipped, and the next dose should be taken at the usual time.
AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg Combination Therapy
When using AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg with insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of insulin / sulfonylurea derivatives in order to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Drug interaction of AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg tablets
Insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives may increase the risk of hypoglycemia, therefore, if the drug is used in combination with insulin or sulfonylurea derivatives, smaller doses of these drugs may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Empagliflozin may increase the diuretic effect of thiazide and loop diuretics and increase the risk of dehydration and hypotension.
Empagliflozin is metabolized mainly by 5’-diphosphoglucuronosyltransferases (UGT); however, clinically significant effect of UGT inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of empagliflozin is not expected. The combined use of empagliflozin with known UGT inducers is not recommended, because when using this combination, the effect of empagliflozin may decrease.
The combined use with rifampicin reduced the effectiveness of linagliptin by 40%, which indicates the possibility of reducing the effectiveness of linagliptin in the case of its combination with active P-gp inducers or cytochrome P450 CYP3A4 isoenzymes, especially if these drugs are used for a long time.
What are the precautions for AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg tablets?
Caution should be used in patients at risk of hypovolemia (use of hypotensive drugs with a history of arterial hypotension); with gastrointestinal diseases leading to fluid loss; use in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives or insulin; infections of the genitourinary system; adherence to a low-carbohydrate diet; diabetic ketoacidosis in the anamnesis; low secretory activity of β-pancreatic cells; in patients over the age of 75 years.
When using sodium-dependent glucose transporter type 2 inhibitors, including empagliflozin, rare cases of diabetic ketoacidosis have been reported. In some of these cases, the manifestations were atypical and expressed in a moderate increase in blood glucose concentration (no more than 14 mmol/l (250 mg/dl)).
The risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis should be taken into account in case of non-specific symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, abdominal pain, pronounced thirst. difficulty breathing, disorientation, unmotivated fatigue or drowsiness. If such symptoms develop, the patient should be immediately examined for ketoacidosis, regardless of the concentration of glucose in the blood. The use of this combination should be discontinued or temporarily suspended until a diagnosis is established.
Patients who may have a higher risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis when taking sodium-dependent glucose transporter type 2 inhibitors include patients who follow a diet with a very low carbohydrate content (because this combination can lead to an increase in the production of ketone bodies), patients with severe dehydration, a history of ketoacidosis or low secretory activity of beta cells. In such patients, the drug should be used with caution. Caution is required when reducing the dose of insulin in insulin-dependent patients.
With the combined use of AjaDuo ® 10mg / 5mg with sulfonylurea derivatives or with insulin, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of the latter due to the risk of hypoglycemia.
Cases of acute pancreatitis have been reported in patients taking linagliptin. In case of suspected pancreatitis, the drug should be discontinued.
The effectiveness of empagliflozin depends on kidney function. Therefore, it is recommended to monitor kidney function before using this combination and periodically during treatment (at least once a year).
Osmotic diuresis accompanied by therapeutic glucosuria, which may occur against the background of the use of sodium-dependent glucose transporter type 2 inhibitors, may lead to a moderate decrease in blood pressure. Therefore, caution should be exercised in cases where a decrease in blood pressure is undesirable, for example, in patients with cardiovascular diseases; patients taking antihypertensive drugs (with a history of arterial hypotension), as well as in patients over 75 years of age.
If a patient taking the drug develops conditions that can lead to fluid loss (for example, in gastrointestinal diseases), the patient’s condition, blood pressure, and hematocrit and electrolyte balance should be carefully monitored. It may require temporary, up to the restoration of the water balance, discontinuation of the drug.
The incidence of side effects such as urinary tract infections was comparable with the use of empagliflozin at a dose of 25 mg and placebo, and higher with the use of empagliflozin at a dose of 10 mg. Complicated urinary tract infections (such as pyelonephritis and urosepsis) they were observed with comparable frequency in patients taking empagliflozin and placebo. In case of complicated urinary tract infections, it is necessary to temporarily discontinue the use of this combination.
Patients aged 75 years and older have an increased risk of hypovolemia, so the drug should be used with caution in this category of patients. The experience of using empagliflozin in patients older than 85 years is limited, therefore, the use of the drug in patients older than 85 years is contraindicated.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and mechanisms
Patients should be careful when driving vehicles and mechanisms, because when using the drug (especially in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives and / or insulin), hypoglycemia may develop.
AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg during pregnancy and lactation
Contraindicated use during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding).
Application of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg in childhood
AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg contraindications for use in children and adolescents under the age of 18.
The use of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg in renal dysfunction
Patients with renal insufficiency with GFR < 45 ml / min / 1.73 m2 are not recommended to use the drug.
Patients with GFR >45 ml/min/1.73 m2 do not need dose adjustment.
The use of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg for liver function disorders
Patients with impaired liver function do not need dose adjustment.
Use of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg in the elderly
The use of the drug in patients older than 85 years is contraindicated.
Combination of Empagliflozin and Linagliptin
The mechanism of action of empagliflozin, independent of insulin metabolism and the functional state of pancreatic beta cells, differs from and complements the mechanisms of action of drugs of other groups currently used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2). Empagliflozin has been found to potentiate the action of all hypoglycemic drugs with other mechanisms of action, including dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Long-term use of a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin resulted in a significant increase in insulin sensitivity, compared with the use of linagliptin and empagliflozin in the form of monotherapy.
Empagliflozin
Empagliflozin is a reversible, highly active, selective and competitive inhibitor of the type 2 sodium-dependent glucose transporter (NRPG-2) with a concentration value required to inhibit 50% of the enzyme activity (IC50) equal to 1.3 nmol.
Empagliflozin does not inhibit the activity of other glucose transporters necessary for the transport of glucose to peripheral tissues, and its selectivity to NPG-2 is 5000 times higher than selectivity to sodium-dependent glucose transporter type 1 (NPG-1), the main transporter responsible for glucose absorption in the intestine.
The glucose filtered in the kidneys is almost completely (up to 90%) reabsorbed with the help of HPG-2 and to a lesser extent with the help of HPG-1, which are located, respectively, in the proximal segments (S1 and S3) of the renal tubules. Empagliflozin, inhibiting the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leads to an increase in its excretion by the kidneys, which causes a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood, both after a single oral administration of the drug and with prolonged use. Empagliflozin improves glycemic indices both on an empty stomach and after meals. In addition, the excretion of glucose by the kidneys causes a loss of calories and leads to a decrease in body weight.
Empagliflozin improves glycemic control in patients with DM2 by reducing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys. The amount of glucose released by the kidneys using this mechanism depends on the concentration of glucose in the blood and the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Inhibition of NRPG-2 in patients with DM2 and hyperglycemia leads to the excretion of excess glucose by the kidneys.
In addition, initiation of empagliflozin therapy leads to an increase in sodium excretion, which causes osmotic diuresis and a decrease in intravascular volume. The mechanism of action of empagliflozin does not depend on the function of beta cells and the insulin pathway, resulting in a low risk of hypoglycemia.
The glucosuria observed during the use of empagliflozin is accompanied by a slight increase in diuresis, which can contribute to a steady and moderate decrease in blood pressure (BP). Glucosuria, natriuresis and osmotic diuresis observed with the use of empagliflozin may contribute to improving cardiovascular outcomes.
Linagliptin
Linagliptin is an inhibitor of the enzyme DPP-4, which is involved in the inactivation of hormones incretins – glucagon-like peptide type 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Linagliptin actively binds to the enzyme DPP-4 (reversible bond), which causes a steady increase in the concentration of incretins and a long-term preservation of their activity.
Linagliptin selectively binds to the enzyme DPP-4 and has 10,000 times greater selectivity compared to the enzymes DPP-8 or DPP-9 in vitro.
GPP-1 and GIP enhance the biosynthesis of insulin and its secretion by beta cells of the pancreas at normal or elevated blood glucose concentrations. In addition, GLP-1 reduces the secretion of glucagon by alpha cells of the pancreas, which leads to a decrease in glucose production in the liver.
Linagliptin increases the glucose-dependent secretion of insulin and reduces the secretion of glucagon, which leads to a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood.
What are the side effects of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg ?
Allergic reactions:
often
- hypersensitivity reactions;
infrequently
- angioedema,
- urticaria.
From the side of metabolism:
often
- hypoglycemia (when combined with sulfonylurea derivatives or insulin).
From the respiratory system:
often
- cough,
- nasopharyngitis.
From the cardiovascular system:
infrequently
- hypovolemia.
From the digestive system:
infrequently
- pancreatitis;
frequency unknown
- ulceration of the oral mucosa.
From the urinary system:
often
- urinary tract infections,
- frequent urination;
infrequently
- dysuria.
From the genital organs and breast:
often
- vaginal candidiasis,
- vulvovaginitis,
- balanitis,
- other genital infections.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissue:
often
- itching;
infrequently
- rash.
Contents
- 1 Buy AjaDuo®10mg/5mg Online
- 1.1 Order AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg Tablet
- 1.2 AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg Dosage
- 1.3 Contraindications AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg:
- 1.4 How to take AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg tablets?
- 1.5 Drug interaction of AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg tablets
- 1.6 What are the precautions for AjaDuo® 10mg/5mg tablets?
- 1.6.1 Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and mechanisms
- 1.6.2 AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg during pregnancy and lactation
- 1.6.3 Application of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg in childhood
- 1.6.4 The use of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg in renal dysfunction
- 1.6.5 The use of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg for liver function disorders
- 1.6.6 Use of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg in the elderly
- 1.7 Combination of Empagliflozin and Linagliptin
- 1.8 What are the side effects of AjaDuo® 10mg / 5mg ?